Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124


ADHD brain training has gained significant traction as an alternative or complementary approach to managing Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) symptoms. In recent years, the search for non-pharmacological treatments has led many to consider cognitive training and brain exercises as viable options. But what exactly is ADHD brain training, and does it really work? This article will explore these questions and more, diving deep into the science of brain training for ADHD adults and children, its benefits, limitations, and how it compares to other treatment methods.

One of the most frequent questions regarding this method is whether brain training for ADHD is effective. The answer, like much in ADHD research, is complex. Scientific studies have shown mixed results, with some indicating improvements in attention and impulse control, while others have found minimal long-term benefits.

The premise of brain training is rooted in the concept of neuroplasticity—the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections. Neuroplasticity allows the brain to adapt to new challenges, and in the case of ADHD, brain training exercises aim to strengthen the brain’s ability to manage attention, impulse control, and memory.
While some studies suggest that brain training can improve ADHD symptoms, it’s essential to recognize that most research indicates that improvements are often task-specific. For example, a child might get better at a particular memory game but still struggle with real-world tasks like homework.

Despite the mixed research, there is anecdotal evidence suggesting that brain training can help ADHD individuals improve their cognitive abilities. For many, brain training serves as a tool to manage symptoms rather than a cure. The repetitive and targeted nature of brain exercises can help improve focus, attention span, and working memory—three key areas where individuals with ADHD tend to struggle.

A variety of brain exercises are tailored specifically to ADHD individuals. These exercises often focus on improving executive functions, such as planning, organization, and self-control. Here are a few common brain exercises for ADHD:
For ADHD adults, brain exercises are often more focused on daily challenges like time management, organization, and emotional regulation. Brain training for ADHD adults typically aims to provide the cognitive tools necessary to manage responsibilities more effectively.

To understand brain training for ADHD better, it’s essential to break down the cognitive aspects of ADHD. ADHD affects key areas of the brain responsible for executive functions. This includes the ability to focus, plan, and execute tasks, control impulses, and regulate emotions. Brain training targets these areas, attempting to strengthen the neural connections that may be underdeveloped or inefficient in people with ADHD.
However, not all brain training is created equal. Programs like Lumosity or Cogmed are designed with specific cognitive goals, but the challenge lies in translating those improvements from the digital space to real-life situations. So, while you may get better at a memory game, that doesn’t necessarily mean you’ll remember to submit an important project on time or manage tasks better in your daily life.
A significant criticism of ADHD brain training is that the gains achieved in controlled exercises don’t always translate into real-world improvements. This phenomenon, known as “task-specific learning,” means that while a person might excel at a particular cognitive exercise, the benefits often don’t extend beyond that specific task.
Despite these limitations, brain training remains a useful tool when combined with other ADHD management strategies, such as medication, behavioral therapy, or lifestyle changes.
While structured ADHD brain training can be beneficial, there are other, more practical ways to “train” your brain to better manage ADHD symptoms. Some alternative methods focus on lifestyle changes and therapies that promote brain health and improve cognitive function.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is one of the most effective non-pharmaceutical treatments for ADHD. Unlike brain training programs that focus on isolated tasks, CBT teaches individuals with ADHD how to modify their thought patterns and behaviors. This can help with everything from impulsivity to emotional regulation and organizational skills.
Mindfulness practices, such as meditation, are increasingly being recognized for their benefits in managing ADHD. These practices encourage individuals to focus on the present moment, which can help improve sustained attention and reduce impulsivity. Studies have shown that mindfulness training can lead to improvements in ADHD symptoms, particularly when practiced consistently over time.
Physical activity is another excellent way to “train” the brain. Exercise has been shown to increase the production of neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine, which are often deficient in people with ADHD. Aerobic activities such as running, swimming, or cycling can help improve attention, reduce hyperactivity, and increase mood stability.
No two individuals with ADHD are alike, and neither are their treatment needs. Whether you’re considering brain training for ADHD adults, children, or a mix of cognitive strategies, the key is finding a method that works for you. Many individuals benefit from a combination of brain training, therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes.
A personalized approach to ADHD management often yields the best results. For example, some individuals might benefit from medication to manage more severe symptoms, while brain training serves as a supplemental tool to improve focus and working memory. Others might find that a mix of mindfulness practices, CBT, and exercise works best for them.
Finding the right balance of treatments can take time and patience. It’s essential to stay open to different methods and to monitor progress regularly to see what’s working and what’s not.
To fully understand brain training for ADHD, it helps to examine the different types of cognitive exercises available. ADHD brain training is often divided into two categories: structured cognitive tasks and lifestyle-oriented brain training activities.
These tasks are designed specifically to target areas of weakness in the ADHD brain, such as working memory, impulse control, and sustained attention. Programs like Cogmed and Lumosity offer structured cognitive training exercises tailored to the unique needs of ADHD individuals.
This type of training involves practical, day-to-day activities that can help manage ADHD symptoms. For example, using a daily planner to organize tasks, breaking projects into smaller chunks, and creating reminders for important activities can all serve as “brain training” in a real-world context.
The effectiveness of brain training for ADHD lies in its ability to harness the brain’s neuroplasticity. By consistently challenging the brain with targeted exercises, individuals with ADHD can improve their cognitive abilities over time.
ADHD brain training typically involves repetitive cognitive tasks that stimulate different parts of the brain. These tasks are designed to gradually build strength in areas like working memory, attention, and impulse control.
For example, a typical ADHD brain training session might involve playing a memory game that requires the user to remember a series of images or numbers in a specific order. Over time, the brain’s ability to retain and recall information improves, which can translate into better working memory in real-life situations.
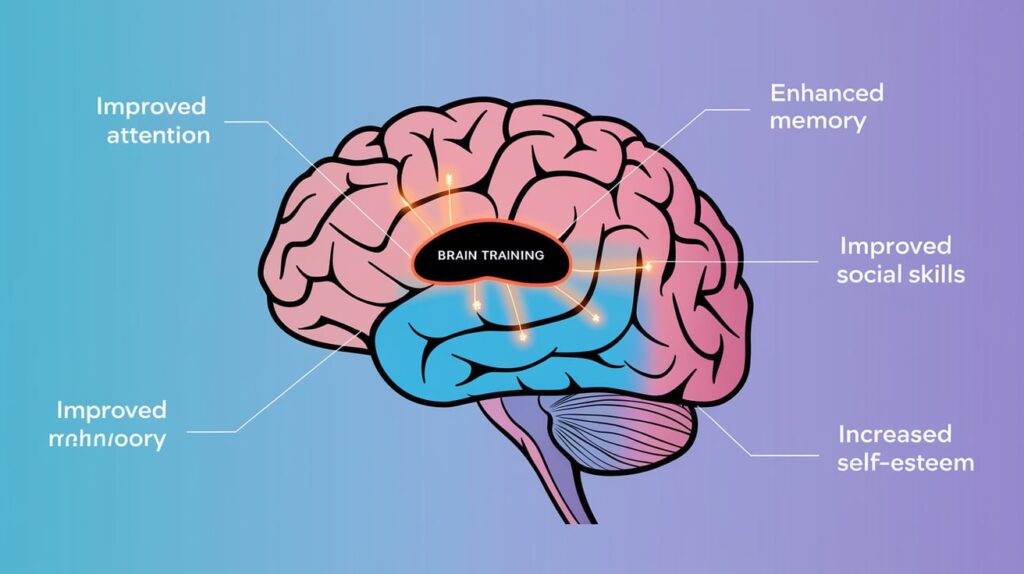
Despite its limitations, brain training for ADHD does offer several potential benefits, particularly when used as part of a broader treatment plan.
One of the most significant benefits of ADHD brain training is an improvement in working memory. This is particularly beneficial for individuals who struggle to remember instructions, keep track of tasks, or manage their responsibilities effectively.
Brain exercises for ADHD aim to lengthen attention spans, allowing individuals to focus on tasks for more extended periods. This can be especially helpful in work or school settings, where sustained attention is critical for success.
By training the brain to delay reactions, individuals with ADHD can improve their impulse control, which is often a significant challenge. Over time, this can lead to better decision-making and less impulsive behavior in social, academic, and professional settings.
Some brain training programs also focus on improving emotional regulation, helping individuals manage mood swings and emotional outbursts more effectively.
Is brain training effective for ADHD? The answer is nuanced. While brain training can provide cognitive improvements, it’s essential to approach it as part of a broader treatment plan rather than a standalone solution. For many individuals, brain training works best when combined with medication, behavioral therapy, and lifestyle changes.
With the rise of technology, many apps now offer brain training for ADHD adults and children. These apps provide tailored programs designed to improve cognitive function through gamified exercises.
One of the most common questions is whether ADHD brain training delivers fast results. The reality is that brain training is not a quick fix. Like physical exercise, cognitive improvements take time, and consistent practice is required to see meaningful progress.
Most brain training programs recommend consistent use for several weeks or months before noticeable improvements occur. For some individuals, changes in attention and impulse control can be seen within a few weeks, while others may take longer.
ADHD primarily affects an individual’s ability to focus and sustain attention on tasks, particularly those that are boring or repetitive. ADHD brain training targets these deficits by providing exercises that gradually build the brain’s ability to maintain focus for more extended periods.
People with ADHD often find it difficult to focus on tasks that don’t immediately capture their interest. This lack of sustained attention can lead to unfinished projects, poor work performance, and frustration. Brain training aims to address this by strengthening the brain’s ability to maintain focus over time.
Yes, brain training can help ADHD by providing structured cognitive exercises that target specific weaknesses in the ADHD brain. However, it’s important to manage expectations and understand that brain training is most effective when combined with other treatments, such as behavioral therapy or medication.
Cognitive training for ADHD is not a one-size-fits-all solution. While some individuals may see improvements in attention, memory, and impulse control, others may find that brain training provides only limited benefits. The key to success is consistency and using brain training as part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
ADHD can significantly impact work performance, particularly in jobs that require sustained attention, organization, and impulse control. Brain exercises for ADHD adults aim to improve these areas, helping individuals stay on task, complete work assignments, and avoid distractions.
Individuals with ADHD often struggle with time management, meeting deadlines, and maintaining focus during long tasks. Brain training exercises can help improve these skills, but it’s also essential to use other strategies, such as organizational tools and external reminders, to manage ADHD symptoms in a professional setting.
Aside from brain training, other strategies can strengthen attention in ADHD individuals. These include creating structured routines, using organizational tools, and breaking tasks into smaller, more manageable steps.

Yes, ADHD brain training is generally considered safe. Since most brain training programs are non-invasive and involve only cognitive tasks, there are no known physical risks. However, individuals should be cautious about expecting dramatic results and consider it a supplement to other treatments.
Memory games, attention-building tasks, and impulse control exercises are commonly used in ADHD brain training programs.
While brain training can help, it is not a replacement for medication. For many, it works best in conjunction with traditional treatments like medication and behavioral therapy.
Consistent practice over weeks or months is often required before noticeable improvements occur.
Brain training is generally safe, but it’s essential to have realistic expectations. It’s not a cure-all, and improvements may be subtle.
In summary, ADHD brain training can be a helpful tool for managing ADHD symptoms, especially when used in conjunction with other treatments like medication and behavioral therapy. While brain training shows promise in improving attention, working memory, and impulse control, it’s essential to approach it with realistic expectations and understand that it’s not a standalone solution. Whether through apps, structured exercises, or other cognitive training methods, the key to success lies in consistent practice and finding the right combination of treatments tailored to the individual.