Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Heart disease remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide, which makes it critical to diagnose any heart-related issues early. One of the most effective ways of identifying heart disease and assessing heart function is through diagnostic tests that evaluate the heart’s performance under stress. Two of the most commonly used tests in cardiology are the stress test and the stress echocardiogram (stress echo). Both tests serve a similar purpose—to evaluate the heart’s function when it’s under stress—but they differ in methodology, procedure, and the information they provide. So, what is the difference between stress test and stress echo?
In this detailed guide, we’ll break down these two procedures, explore how they differ, what they detect, and the reasons why one might be recommended over the other. Whether you’re undergoing these tests or simply trying to understand more about heart health diagnostics, this article will provide you with all the information you need.
A stress test, also known as an exercise stress test or treadmill test, evaluates how your heart functions during physical exertion. It is one of the most common diagnostic tools used to detect coronary artery disease, heart attacks, arrhythmias, and other heart-related issues. The purpose of a stress test is to monitor the heart’s activity while it’s being stressed through physical exercise.
A traditional stress test involves a patient walking on a treadmill or riding a stationary bike. As the patient exercises, the intensity gradually increases, forcing the heart to work harder. Electrodes are attached to the chest to monitor the heart’s electrical activity (ECG), and the blood pressure is measured regularly. The doctor or technician will look for changes in heart rate, rhythm, and the overall response to exercise.
The stress test continues until the patient reaches a target heart rate, experiences symptoms like chest pain, or can no longer continue due to exhaustion or discomfort. The test usually lasts between 10 and 15 minutes, depending on the patient’s fitness level and tolerance.
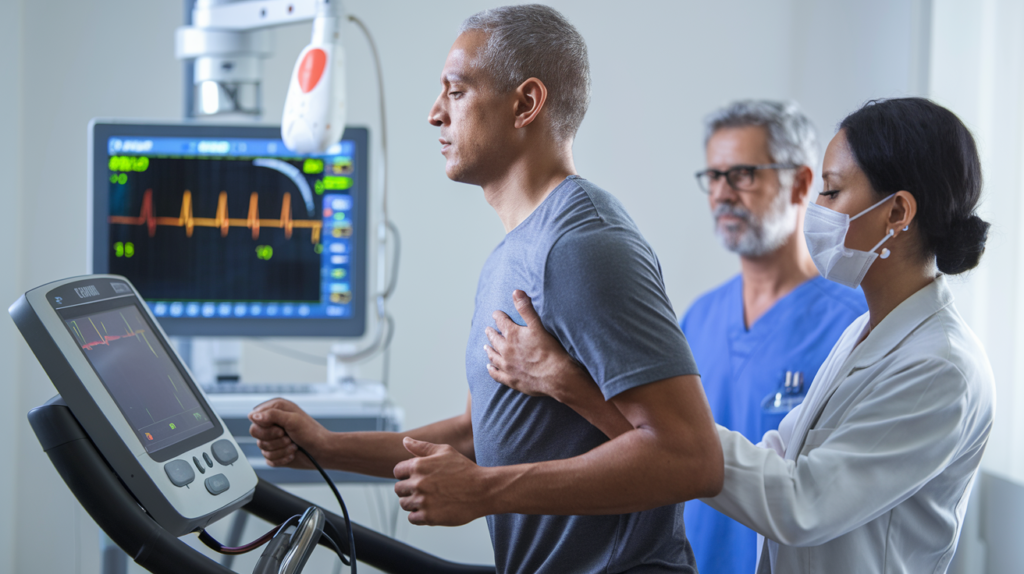
A stress echocardiogram (stress echo) is an advanced form of the stress test. It combines the traditional exercise stress test with an echocardiogram, a diagnostic imaging technique that uses ultrasound to create detailed images of the heart’s structure and function. This procedure allows doctors not only to monitor heart activity but also to visualize how well the heart is pumping blood and how the heart’s chambers, valves, and muscles are functioning under stress.
Similar to the standard stress test, a stress echo involves the patient exercising on a treadmill or stationary bike. However, in addition to monitoring the heart’s electrical activity, ultrasound gel is applied to the chest, and an ultrasound probe is used to take real-time images of the heart. The images captured before and after the stress period are compared to evaluate any changes in heart function and structure.
Doctors look for changes in heart muscle movement, blood flow, and valve function, as these are key indicators of coronary artery disease, myocardial ischemia (reduced blood flow to the heart), and other heart conditions.

While both tests involve monitoring the heart under physical stress, there are several critical differences between a stress test and a stress echo. Let’s break down these differences:
There are different types of stress tests available depending on the patient’s condition and ability to exercise. Here are the most common variations:
This is the most common form of stress test, where the patient exercises on a treadmill or stationary bike. The intensity gradually increases as the test progresses.
For patients who cannot exercise due to physical limitations, a pharmacological stress test can be used. This involves administering medication such as adenosine or dobutamine, which stimulates the heart to beat faster and work harder, simulating the effects of exercise.
A nuclear stress test is similar to a standard stress test but includes a special dye injected into the bloodstream. This dye is tracked using a special camera that captures detailed images of blood flow to the heart muscle, providing more information on areas with reduced blood flow.
A stress echo may be recommended for patients with risk factors for heart disease or those experiencing symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, or fatigue. It’s especially beneficial for patients who have already been diagnosed with heart disease or are recovering from a heart attack. It helps doctors evaluate the extent of heart damage, identify blockages in the coronary arteries, and assess the function of the heart valves.
Additionally, a stress echo is helpful for patients who are at high risk for cardiovascular issues but cannot undergo a standard stress test due to physical limitations.
Before the test, you will be asked to avoid eating or drinking for several hours. Electrodes will be attached to your chest to monitor heart activity, and ultrasound gel will be applied to your chest to take images of the heart. As you exercise, images will be captured before, during, and after exercise.
The procedure typically takes between 30 and 60 minutes, and you will be monitored closely throughout the process. Afterward, you can resume normal activities unless your doctor advises otherwise.
Q1: What is the difference between stress test and stress echo in terms of diagnostic accuracy?
Stress echo is more accurate as it provides detailed visual images of the heart, allowing doctors to assess both heart function and structure, which is not possible with a standard stress test.
Q2: Can a stress echo detect heart disease in people without symptoms?
Yes, a stress echo can detect coronary artery disease, valve dysfunction, and other heart issues even in patients without symptoms, which makes it an important tool for early detection.
Q3: How long does it take to recover from a stress echo?
There is typically no recovery time required. Patients can return to normal activities immediately after the test unless otherwise advised by their doctor.
So, what is the difference between stress test and stress echo? A stress test is a simpler, quicker method to assess how the heart responds to physical activity, primarily focusing on the heart’s electrical activity. On the other hand, a stress echo combines the traditional stress test with echocardiography, providing detailed images of the heart’s structure and function under stress. This makes the stress echo a more comprehensive diagnostic tool, particularly for patients with suspected coronary artery disease or heart valve problems.
Each test has its own unique advantages and is used for different diagnostic purposes, depending on the patient’s health condition and the information needed by the doctor. If you are concerned about your heart health, consult your doctor to determine which test is most appropriate for your situation.